 |
|
 |
|
|
Vitamin B5 -- Pantothenic Acid |
|
Structure |
The Chemical Name of Pantothenic Acid is: d(+)-a-(-dihydroxy-b,b-dimethylbutyryl-b-alanine)
The structure of Vitamin B5 is as follows:
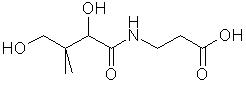
http://www.chm.bris.ac.uk/webprojects2002/schnepp/pantothenic.html
Pantothenic acid belongs to the group of B vitamins. The name is derived from the Greek words meaning "from everywhere" Earlier names were vitamin B5, antidermatosis vitamin, chick antidermatitis factor and chick antipellagra factor. The naturally occurring form is D-pantothenic acid.
Pure pantothenic acid is a viscous hygroscopic oil that is chemically not very stable. Supplements therefore usually contain the calcium salt or the alcohol, panthenol. Both are highly water soluble and are rapidly converted to the free acid in the body. Calcium pantothenate is often included in multivitamin preparations; panthenol is the more common form used in monopreparations, which are available in a wide variety of pharmaceutical forms (e.g. solutions for injection and local application, aerosols, tablets, ointments, creams)

http://www.coenzyme-a.com/pantothenic.html