|
Structure and Function
|
|
|
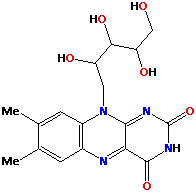
Above is the structure of Riboflavin. Its formula is C17H20N4O6. Vitamin B2 is the paraent compound of flavins. It combines in the tissues with phosphoric acid to form two forms of flavins - FAD (Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide) and FMN (Flavin Mononucleotide). These two forms act as hydrogen carriers in several important oxidative systems (oxidation/reduction reactions) in the body. Functions: -metabolizes amino acids, fatty acids, and carbohydrates to provide energy for the body -acts as antioxidants to neutralize free radicals in the body -activates Vitamin B6, converts tryptophan to niacin, and form red blood cells -produces antibodies -responsible for cell respiration and body growth -is used to prevent and treat cataracts and migraines -helps recovery from serious burns -alleviates stress and depression associated with eating disorders -treats preeclampsia in pregnant women -beneficial to protein structure such as skin, nail, hair, as well as eyes, mouth, liver, and nervous system
|
|