There were a number of results gathered over the years by cathode ray tube researchers.
1) If an object is placed in the path of the cathode ray, a shadow of the object is cast on the glowing tube wall at the end. This showed that the cathode rays traveled in straight lines.
2) The cathode ray can push a small paddle wheel up an incline, against the force of gravity. This showed that the cathode ray carried energy and could do work.
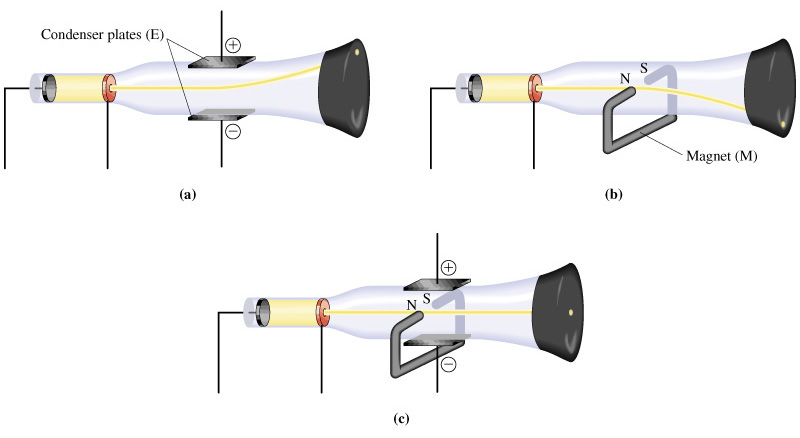
3) The cathode ray is deflected from a straight line path by a magnetic field, suggesting that the two were related in some way. The discovery of this effect in 1855 predates by some ten years the unification of electricity and magnetism by James Clerk Maxwell.
4) Although there was some speculation that the cathode rays were negatively charged, it is not shown to be true by experiment until 1895, just two years before Thomson announces the electron.
5) J.J. Thomson is the first individual to succeed in deflecting the cathode ray with an electrical field. He did so in 1897. The cathode rays bend toward the positive pole, confirming that cathode rays is negatively charged.
