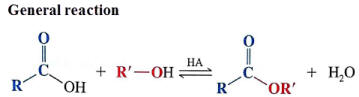
Condensation reaction
|
10.2i- Write the equation for the condensation reaction of an alcohol with a carboxylic acid, in the presence of a catalyst (e.g. concentrated sulfuric acid) to form an ester |
Esterification (Fischer-Speier esterification) is a reflux reaction producing an ester from a carboxylic acid and alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst (H2SO4 or HCl).


Keys:
1. increasing [reactant] can shift the equilibrium to product formation, either the carboxylic acid or alcohol.
2. removing water using a drying agent (anhydrous Na2SO4 or MgSO4) can shift equilibrium to product formation
3. the carbonyl donates the -OH and the hydroxyl donates the -H (evidence by 18O labeled reactions-see here)
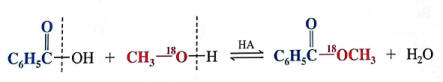
4. steric hindrance can affect the reaction rate--highly substituted alcohols or carboxylic acids reduce reaction rates.
-3o alcohols can lead to acid-catalyzed elimination reactions.
Mechanism:
-The mechanism is described as an acid-catalyzed nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction at the acyl carbon.
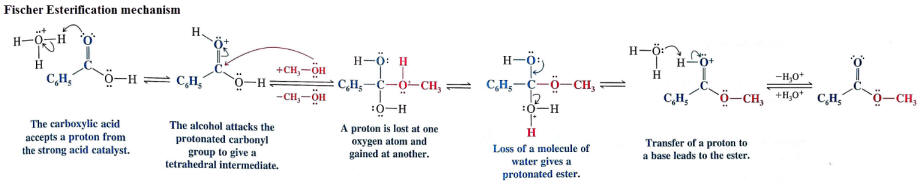
- the forward reaction is described as an acid-catalyzed esterification of an acid, controlled by increasing [alcohol] and removing H2O
- the reverse rection is an acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of an ester, controlled by increasing [H2O] (i.e. diluting the acid).
Video- Fischer esterification mechanism
Video: Esterification lab- UGA
Uses of esters
1.
Esters
that are have fragrant odors are used as a constituent of perfumes, essential
oils, food flavorings, cosmetics, etc
2. Esters are
used as an organic solvent
3. Natural esters are found in pheromones
4. Naturally
occurring fats and oils are
fatty acid esters of glycerol
5.
Phosphodiesters form the backbone of DNA molecules
6.
Nitrate esters, such as nitroglycerin, are known for their explosive
properties
7. Polyesters
are used to make plastics
8. Esters are
used to make surfactants E.g. soap, detergents