
6.4 Gas Exchange--Respiratory system
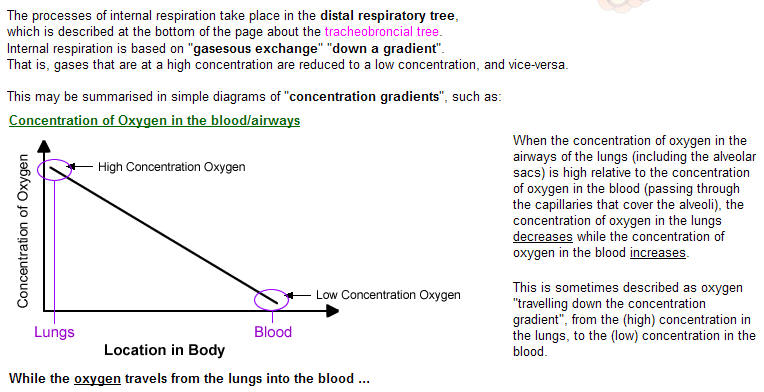
A respiratory systemīs function is to allow gas exchange. The space between the alveoli and the capillaries, the anatomy or structure of the exchange system, and the precise physiological uses of the exchanged gases vary depending on the organism. In humans and other mammals, for example, the anatomical features of the respiratory system include airways, lungs, and the respiratory muscles. Molecules of oxygen and carbon dioxide are passively exchanged, by diffusion, between the gaseous external environment and the blood. This exchange process occurs in the alveolar region of the lungs.
 |
 |
|
 |
||
6.4.1 Ventilation--gas exchange -- cellular respiration
breathing animation- http://health.howstuffworks.com/adam-200020.htm
 |
Ventilation- physical exchange of gases Inspiration (inhalation)- breathing in by contracting the diaphragm, expanding the lungs and letting air move in. Exhalation- breathing out by relaxing the diaphragm, compressing the lungs and forcing air out. |
| Gas Exchange- two different exchanges systems 1. occurs between capillaries and alveoli of the lungs 2. occurs between capillaries and cell membranes within specific tissues
|
|
| Cellular Respiration
|
Gas Exchange animation: http://www.bmu.unimelb.edu.au/examples/gasxlung/
Oxygen binding animation: http://media.pearsoncmg.com/bc/bc_marieb_ehap_8/activities/chapter13/Act13B.html
 |
|
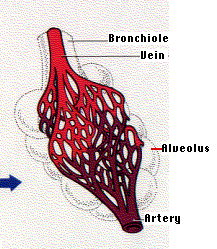 |
6.4.2 - Ventilation system - need
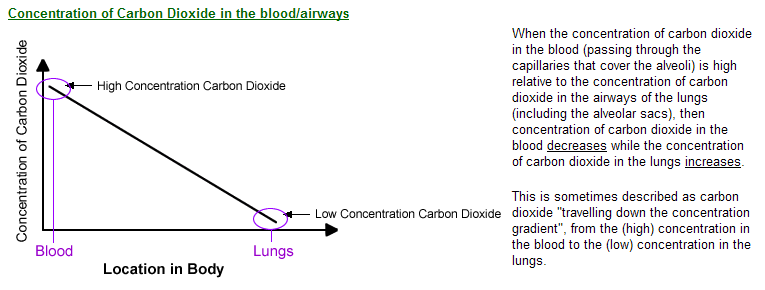
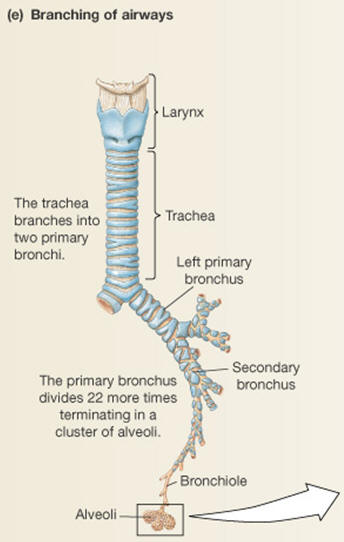
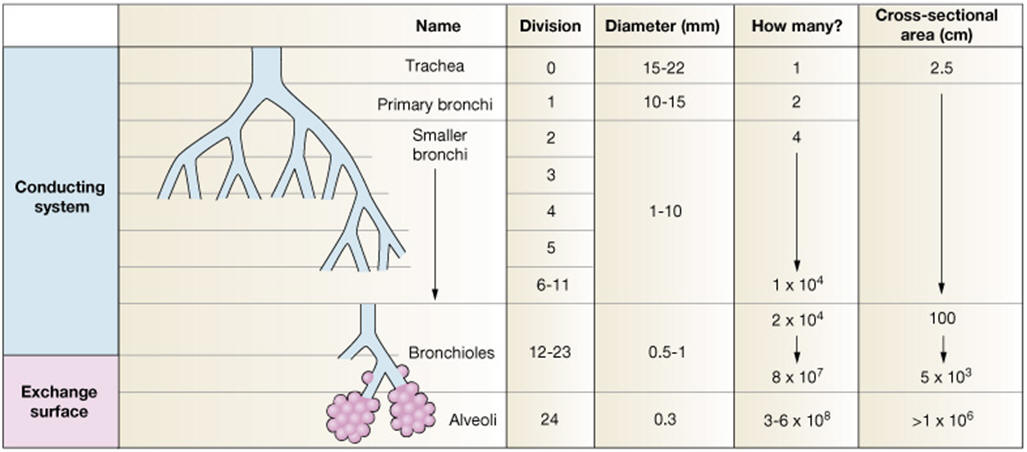
6.4.3 - Alveoli
 |
An alveolus is an anatomical structure that has the form of a hollow cavity. Found in the lung, the pulmonary alveoli are spherical outcroppings of the respiratory bronchioles and are the primary sites of gas exchange with the blood. Alveoli are particular to mammalian lungs. Different structures are involved in gas exchange in other vertebrates |
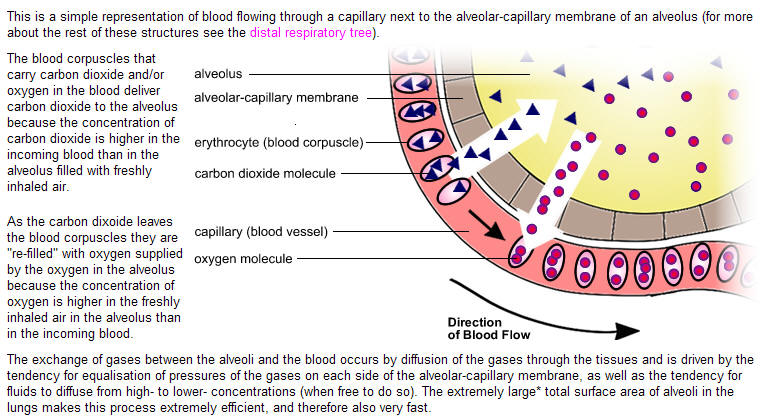
6.4.4 - Ventilation system

6.4.5- Ventilation mechanism
Ventilation animation: http://msjensen.cehd.umn.edu/1135/Links/animations/Flash/0034-swf_alveolar_press.swf