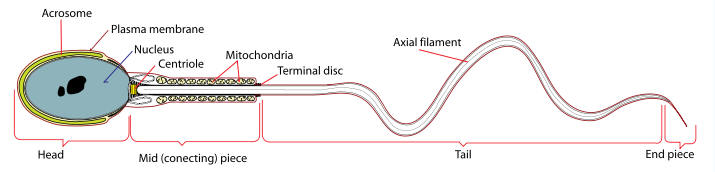
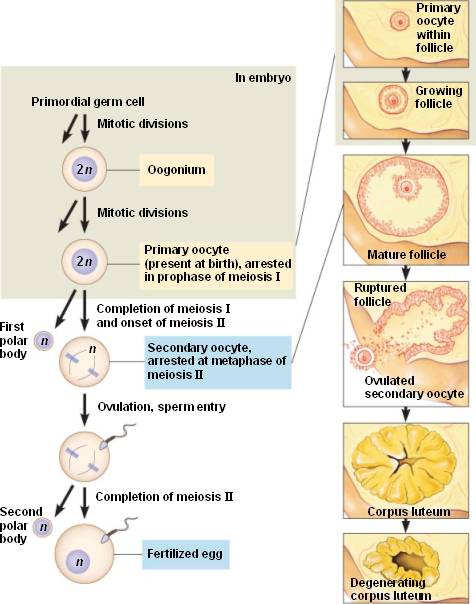
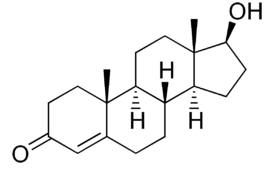
Pre- Peripubertal effects. Pre-
Peripubertal effects are the first visible effects of
rising androgen levels at the end of childhood, occurring in both boys and
girls.
·
Adult-type body odour
·
Increased oiliness of skin and hair, acne
·
Pubarche (appearance of pubic hair)
·
Axillary hair
·
Growth
spurt, accelerated bone maturation
·
Develop hair on upper lip and
sideburns.
Pubertal effects. Pubertal effects begin to occur when androgen has
been higher than normal adult female levels for months or years. In males
these are usual late pubertal effects, and occur in women after prolonged
periods of heightened levels of free testosterone in the blood.
·
Enlargement of sebaceous
glands. This might cause acne.
·
Phallic enlargement or clitoromegaly
·
Increased libido and
frequency of erection
or clitoral engorgement
·
Pubic hair extends to thighs and up toward umbilicus
·
Facial
hair (sideburns,
beard, moustache)
·
Chest hair,
periareolar
hair, perianal
hair
·
Leg hair & Axillary hair (underarm)
·
Subcutaneous fat in face decreases
·
Increased muscle strength and mass
·
Deepening of voice
·
Increase in height
·
Growth of the Adam's
apple
·
Growth of spermatogenic tissue in testes, male fertility
·
Growth of jaw, brow, chin, nose,
and remodeling of facial bone contours
·
Shoulders become broader and rib cage expands
·
Completion of bone maturation and termination
of growth. This occurs indirectly via estradiol metabolites
and hence more gradually in men than women.
Adult testosterone effects. Adult testosterone effects are more clearly demonstrable in
males than in females, but are likely important to both sexes. Some of these
effects may decline as testosterone levels decline in the later decades of
adult life.
·
Libido and clitoral engorgement/penile
erection frequency.
·
Regulates acute HPA
response under dominance challenge
·
Mental and physical energy
·
Maintenance of muscle trophism
·
The most recent and reliable studies have
shown that testosterone does not cause Prostate
cancer, but that it can increase the rate of spread of any existing
prostate cancer. Recent studies have also shown its importance in
maintaining cardiovascular health.
·
Under dominance challenge, may play a role in
the regulation of the fight-or-flight response