Structures of Vitamin K
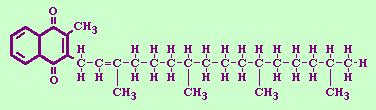
This is the structure of inactive Vitamin K-1
The structure of active Vitamin K-1 is similar to the inactive structure. It has hydroxyls bonded to 1 and 4 instead of double bonded oxygens. This is because it is a hydroquinone--the reduced form of p-Benzoquinone. When a quinone is hydrogenated, it becomes a 1,4-Benzenediol. Once Vitamin K-1 has been reduced to a hydroquinone it is able to convert to a 2,3-epoxide form.