D E F I C I E N C Y ... L E A D S T O . .
-
Reduced growth and appetite
- black tongue (dogs)
- spectacle eyes (chicken)
- PELLEGRA --
- "rough skin" - dermatitis
- Casal's necklace and diarrhea
- anxiety, dementia, delirium
Decreased energy
- Problems with maintaining the integrity
- of the skin and intestinal tract
- skin irregularities
- fatigue, anorexia, weakness
- dizziness
T O X I C I T Y . . . L E A D S T O . .
Acanthosis appearance: contraindication for continued niacin treatment; association with insulin resistance
Hyperuricemia
Hypotension, especially in patients receiving antihypertensive medication
M A J O R I N H I B I T O R S
The HMG Co-A Reductase which utilizes niacin is inhibited by lovastatin, pravastatin, simvastatin, and fluvastatin.
niacinogen (corn) which binds niacin tightly and makes it unavail to absorpt.
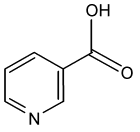 <--- NICOTINIC ACID
<--- NICOTINIC ACID
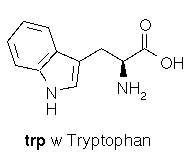
60 MG TRYPTOPHAN = 1 MILLIGRAM OF NIACIN
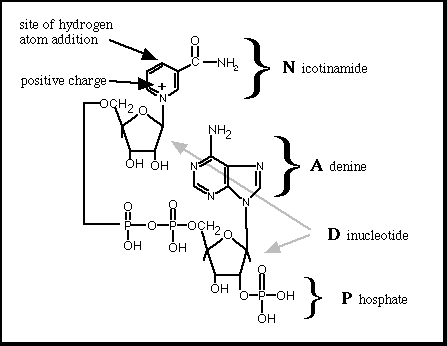
At the bottom is a picture of NAD/NADH. This active coenzyme uses its oxidative/reductive ability in many biochemical reactions.
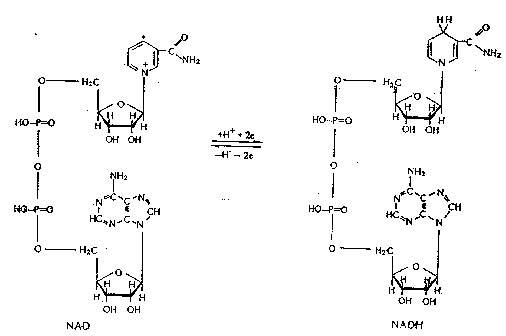
At the bottom is a picture of NADP/NADPH. This other active coenzyme form differs from NAD/NADP because of an additional phosphate. As we can see, its name parallels its structure to a great extent.